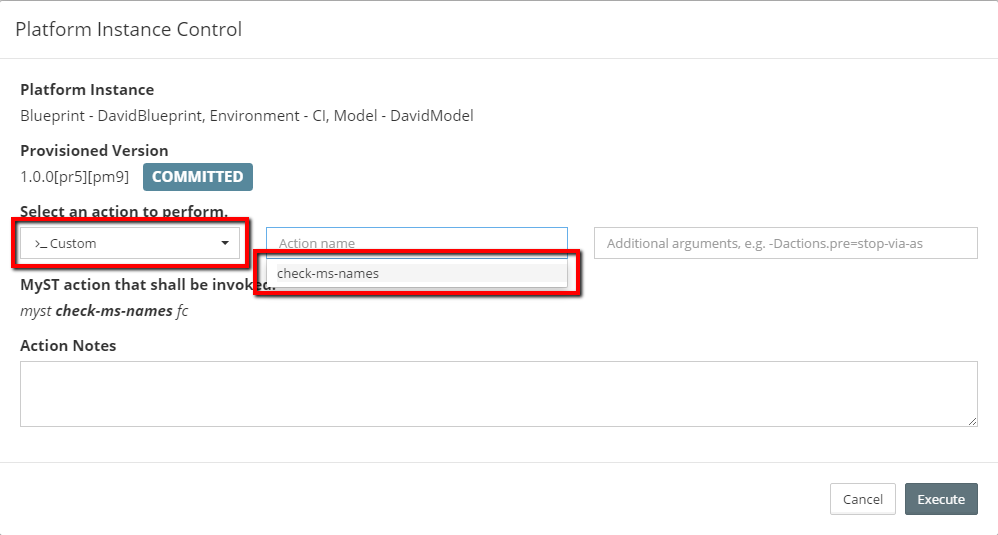
MyST provides a flexible alternative to out-of-the-box MyST actions by allowing the use of custom actions. Administrators can create scripts which are tailored to their purposes.
Understanding Custom Actions
MyST supports the use of Custom Actions within various parts of the Provisioning and Deployment workflow.
When using the CLI, custom actions should be defined and version-controlled under a specific folder within the MyST workspace depending on the language they are written in:
| Language | Location | File Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Python / Jython | ext/targets/jython | .py |
| WLST Script | ext/targets/wlst | .py |
| Java Archive | ext/lib/thirdparty | .jar |
| Puppet Manifest | ext/lib/puppet | .pp |
When using MyST Studio, the actions can be defined directly within the web console and MyST will handle the placement of these files at runtime.
The following property notation can be used to define these actions before or after specific out-of-the-box MyST actions:
action.<ACTION NAME>.pre|post
For example, to execute a configure-mediator action after the update action is complete we could set the following:
action.update.post=configure-mediator
Comparing Jython and WLST Custom Actions
In terms of the scripting language and how it interacts with MyST, the Jython and WLST actions are all quite similar. The differences are as follows:
- Jython code is written in Python but it runs in the Java Virtual Machine so has native access to Java Objects
- WLST code is written in Jython so it has access to the additional WebLogic functions. WLST actions have a dependency on WebLogic being installed so if you do not need access to the WebLogic functions you should opt for a Jython action.
Naming MyST Custom Actions
The action name will be the same name as the file, without the file extension. For example, if the file is called configure-mediator.py, then the action name will be configure-mediator.
Accessing instance data from a Custom Action
At runtime, MyST passes all of the instance data via the conf context. In a case where the values to be set in the action are either different per environment or could be changed often, it's recommended to externalise them into your model.
The runtime data can be accessed either as name/value properties or XMLBean Java objects.
Example WLST Custom Action
def myst(cfg):
"""Display the Domain's Managed Server Names"""
# Log to MyST INFO
LOG.info('hello world')
# Log to MyST DEBUG
LOG.debug('hello debugged world')
# Connect to Admin Server
if 'admin.host' in cfg and 'admin.port' in cfg and 'core.fmw.admin.username' in cfg and 'core.fmw.admin.password' in cfg:
LOG.info('Connecting to Admin Server')
admin_server_url=cfg['admin.host'] + ':' + cfg['admin.port']
connect(cfg['core.fmw.admin.username'],cfg['core.fmw.admin.password'],admin_server_url)
domainRuntime()
# Log the Managed Server names
if 'servers' in cfg:
servers=cfg['servers']
serversList=servers.split(',')
for server in serversList:
LOG.info('Server Name: ' + cfg['core.domain.server[' + server + '].name'])
disconnect()
Creating Custom Actions in MyST Studio
- Click Administration > Custom Actions > Create New
Fill in the mandatory/optional fields
- NOTE - 'Name' becomes the myst custom action name
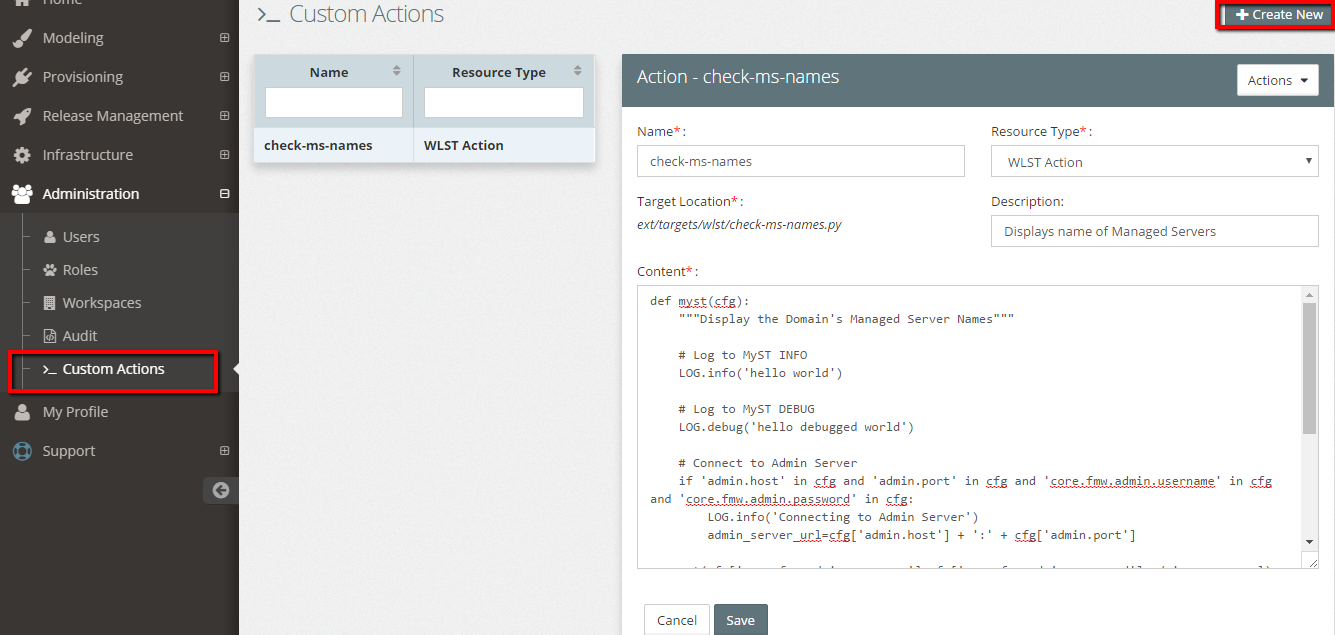
- NOTE - 'Name' becomes the myst custom action name
Run the custom action against your platform instance
Preventing unauthorized changes to Custom Actions
As Custom Actions may contain logic that can affect the state of a given platform or application, it is important that they are governed accordingly. Consider restricting direct edit access and allowing changes to a Custom Action via authorized individuals only either directly or as a push from a version control system.
Any user that is not an API user or System Administrator will be unable to view or edit custom actions. It is generally considered a good practice to give individuals user accounts with non-System Administrator access and assigning explicitly defining the roles.
(Optional) Automating the creation and updates of Custom Actions
It is a general good practice to store MyST custom actions in your version control system such as Git or Subversion.
We can also optionally establish automation to deploy our verified MyST Custom Actions into the MyST Studio console. To do this we need to:
- Retrieve a MyST API Key
- Use our API Key to interact with the REST APIs for creating and updating MyST Custom Actions
Retrieve an API Key
- Login to MyST Studio with an administrator account
- Click on "Administration" then select "Users"
- Under the MySTAdministrator (API User) click on drop-down and select "Show API Key"
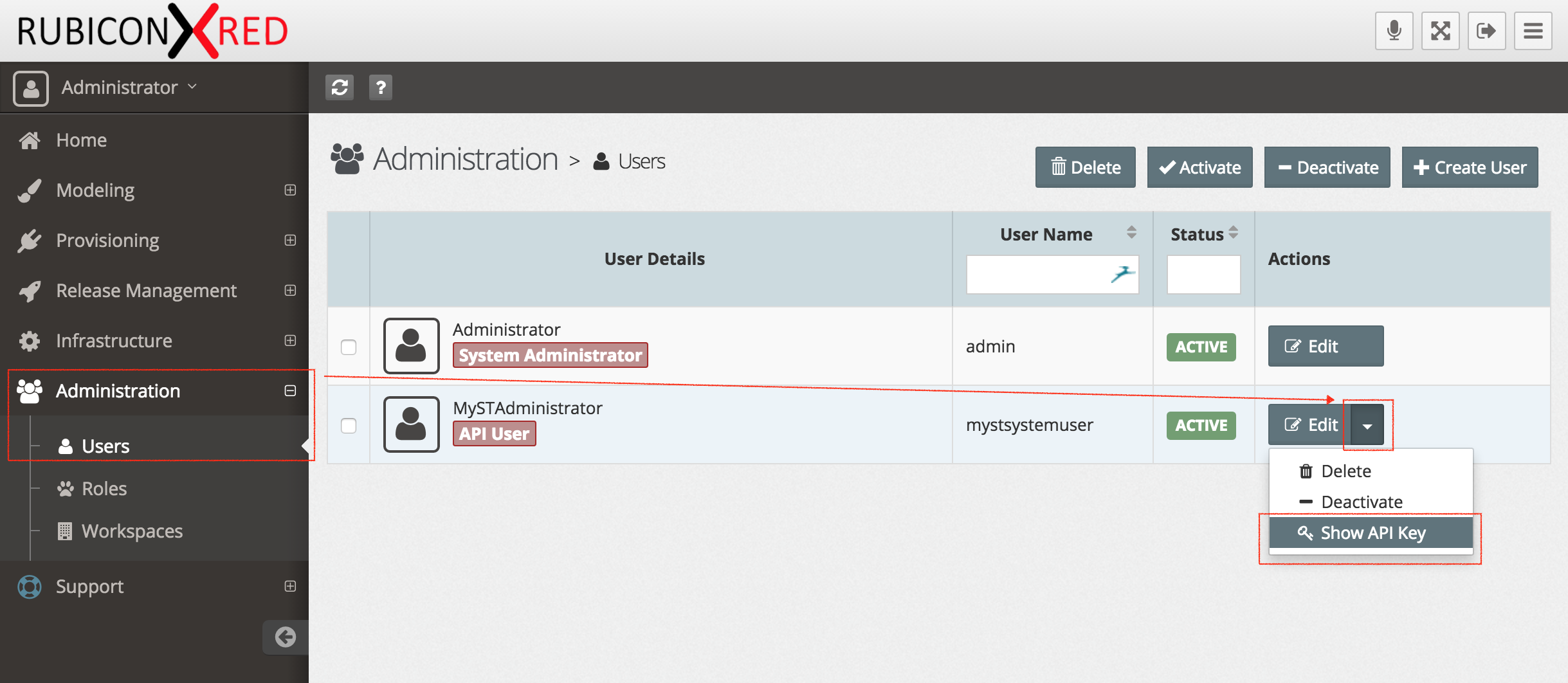
- Copy the key, we will use this later. If you want, you can generate a new key at any time.
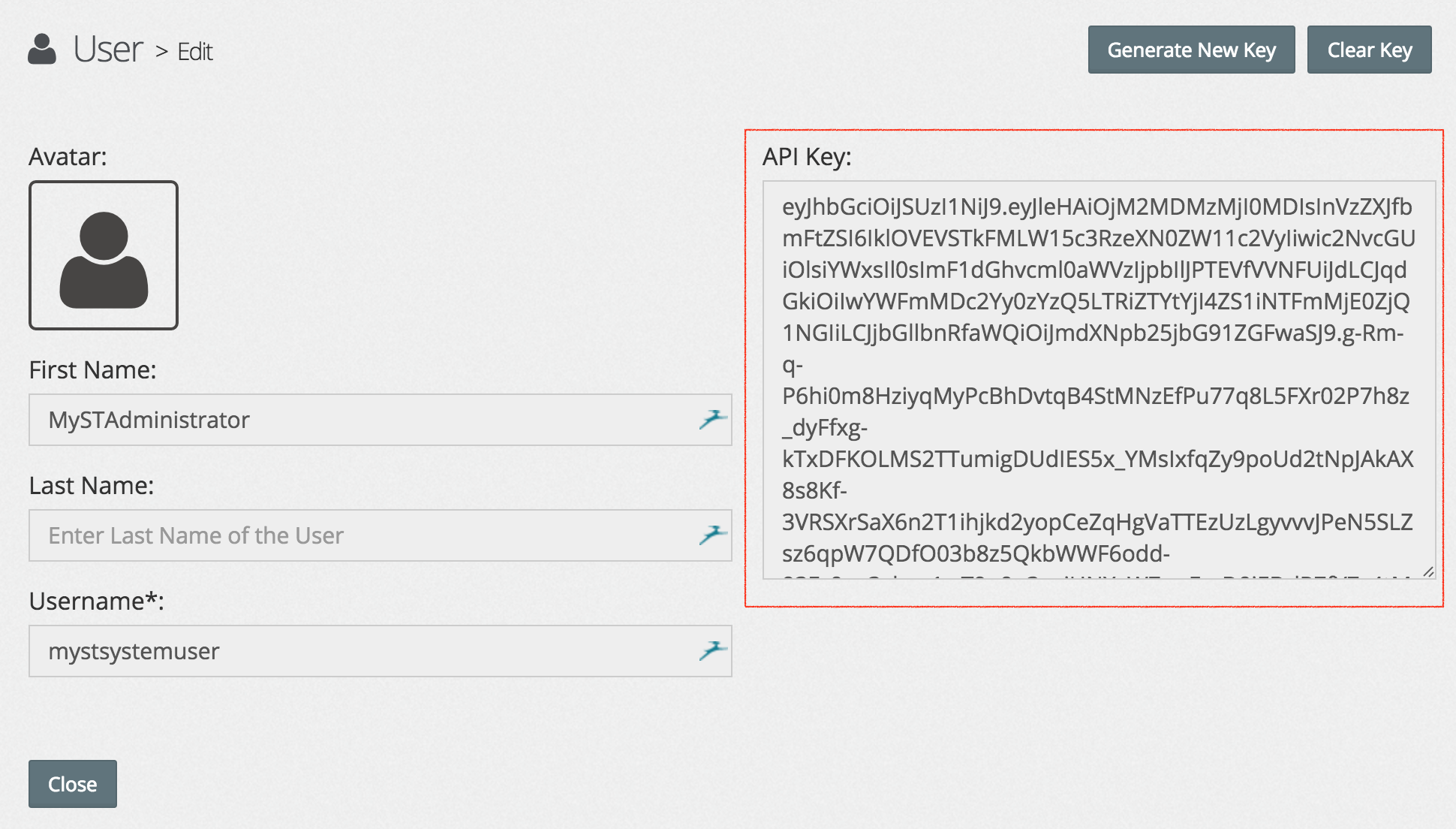
- Let's set an environment variable called
MYST_TOKENwith our API Key, we will use this later in ourcurlscripts that interact with the REST API.
Creating a MyST Custom Action via the REST API
We will need to provide our MyST Custom Action as a string within our JSON payload. The string must have newlines as \n and tabs as \t.
For example, given hello-world.py with the contents
def myst(cfg):
print 'Hello World'
In our string representation it would look like this
def myst(cfg):\n\tprint 'Hello World'
We can assign this to a variable called FILE_CONTENTS that we will use in our REST call.
FILE_CONTENTS="def myst(cfg):\n\tprint 'Hello World'"
In our REST call we will create a new Custom Action called Hello Worldwith theFILE_CONTENTS`
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type:application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $MYST_TOKEN" \
-d "{\"type\": \"JYTHON_ACTION\",\"content\": \"${FILE_CONTENTS}\",\"name\": \"Hello World\",\"description\": \"Hello World Action\",\"relativePath\": \"ext/targets/jython/hello-world.py\"}" http://localhost:8085/api/v1/metadata/myst-custom-actions
Updating a MyST Custom Action via the REST API.
To update an existing action we can use the same REST call as we used with POST but with PUT operation instead.